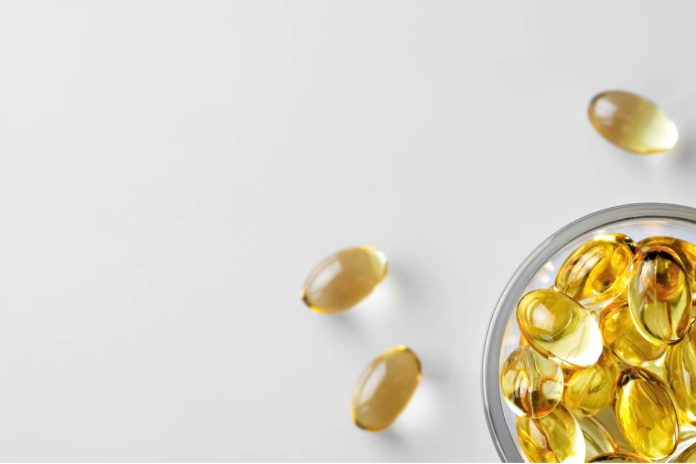
The human body can make most types of fats it needs from other fats in the diet, however, this does not apply to omega-3 fatty acids. Indeed, omega-3 fatty acids are essential nutrients that we cannot make from scratch, but rather must be supplied through diet and/or supplementation. There are several different omega-3s, but the majority of research has focused on three: alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).
These essential fats play a central role in nearly every aspect of health including healthy mood balance, eye health, brain development, and cognitive function, as well as help reduce the risk of heart disease, improve symptoms of ADHD, fight inflammation, help control asthma, and improve liver health. Omega-3s are in every way, crucial to health.
Can’t get enough Omega-3s from Food
Foods high in omega-3 include vegetable oils, nuts, flax seeds, flaxseed oil, leafy vegetables, and fatty fish. Unfortunately, the evolution of the human diet over the past 10,000 years has led to considerable changes in dietary fatty acid composition, predominately omega-3 fatty acids. The diets of our ancestors which consisted primarily of wild plant and animal foods abundant in ALA, EPA, and DHA, have largely been replaced by a diet abundant in refined grains, as well as oils and fats rich in pro-inflammatory omega-6 fatty acids, while deficient in omega-3s.
Though increasing one’s intake of fatty fish is a great way to increase our omega-3 status, it would be nearly impossible to consume enough fish daily to consistently obtain a therapeutic dose of omega-3s via diet for optimal health.
Fish can be toxic
Beyond the prohibitive volume of fish you would be required to eat to supply a sufficient amount of omega-3s daily, we have to consider pollution, and the fact that many fish contain high levels of toxins such as methylmercury – a highly toxic heavy metal, that can cause serious health problems when it reaches a certain level in the body. The amount of mercury in any given fish and other seafood is highly dependent on the species and the pollution in its environment.
As a general rule, larger fish that have a longer lifespan, such as shark, swordfish, tuna, marlin, mackerel, and northern pike – tend to have the most mercury. Conversely, smaller fish such as sardines, anchovies, sole, and trout, contain fewer toxins – most notably, mercury. Fortunately, omega-3 supplements abound and are an ideal way to top up on these essential fatty acids.
Checklist for a quality omega-3
As in all things, not all omega-3 supplements are created equal. Below is a checklist of what to look for to make sure you’re getting only the highest quality omega-3 supplement:
- Molecularly Distilled – Molecular distillation is a process that removes heavy metals, pesticides, and PCBs from fish oils. All quality manufacturers employ this technique to remove potential contaminants before proceeding with their chosen concentration method—be it further molecular distillation, enzymatic processing, or CO2 extraction.
- Long Expiry Date – Most omega-3s state a shelf life of roughly 24 months from the date of manufacturing if they are unopened or exposed to bright light or sources of heat. Even if fish oil supplements are not expired, they can become rancid if stored improperly. Storing your omega-3 supplement in the fridge or freezer can also help keep it fresh and dry and prolong shelf life.
- Glass Bottle – If you opt for a liquid form of omega-3, it’s important to select one that is presented in an amber-colored glass bottle which provides excellent UV protection for the contents and absorbs the most comprehensive range of light waves. This is important because UV rays can change the components of omega-3s.
- Enteric Coating – If capsules are more up your alley, make sure to choose a blend that is enteric-coated as this will protect the softgels/capsule from the harsh environment of the stomach. It will then be able to travel to the small intestine where it can be digested and its fatty acids released and absorbed. Another benefit of enteric coating is that it helps prevent the fishy aftertaste and odor that can accompany certain fish oils.
- Norwegian Sourced – Fish oil from Norway is recognized as the purest and richest source of omega-3s and ranks at the top of the list on the market because of its high concentration of DHA. The oil is extracted from deep cold-water fish in Norway, where there is minimal pollution and an abundance of plankton – the primary source of omega-3 fatty acids.
- High DHA – The brain is a fatty organ, with 10% to 20% of its total fats being DHA. Even more importantly, roughly 90% of the polyunsaturated fatty acids in the brain are DHA
and principally concentrated in the brain’s gray matter. This is why it’s important to select an omega-3 supplement that supplies a high concentration of DHA to support optimal brain and nervous system health throughout life.
Disclaimer: The information in this article is intended for educational and informational purposes only and should not be considered as a substitute for medical advice. Please consult your practitioner prior to taking herbs or nutritional supplements.
Author Bio
Roos Jonsin is a Canadian naturopath and researcher dedicated to helping people live healthier lives through education about vitamins, herbs, and nutritional supplements. Roos also consults with suppliers and manufacturers with product development and marketing. National Nutrition is Canada’s leading health & nutritional supplements store, also voted as the Best Health Food Store in Canada by the experts at Canadian Health Food Association.